Spring总结1:Bean容器及装配Bean
最近将之前关于Spring的书重新拿出来温故一番,并进行总结。
Bean容器
Spring的Bean容器其实不止一个,归结起来可以分为2类:
- Bean工厂(由org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory接口定义),是最简单的Bean容器,提供基本的DI支持;
- 应用上下文(由org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext接口定义),基于BeanFactory构建,提供应用框架级别的服务。
常用应用上下文
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:从一个或多个基于Java的配置类中加载Spring应用上下文;AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext:从一个或多个基于Java的配置类中加载Spring Web应用上下文;ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从类路径下的一个或多个Spring的XML配置文件中加载应用上下文;FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从文件系统下的一个或多个Spring的XML配置文件中加载应用上下文;XmlWebApplicationContext:从Web应用下的一个或多个Spring的XML配置文件中加载应用上下文。
Bean生命周期
下面的生命周期原创图流程图(本人花了一个多小时手工制作。)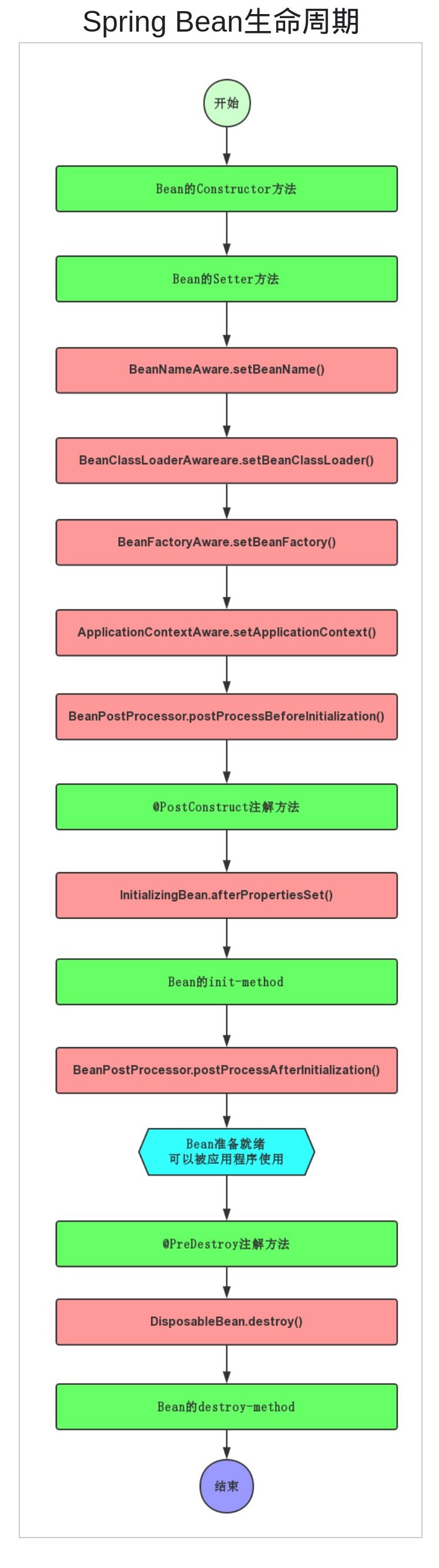
Bean初始化的过程
- Bean的Constructor方法:Spring调用Bean的构造方法,对Bean进行实例化;
- Bean的Setter方法:Spring根据Bean的依赖,执行Bean的Setter方法进行设置属性;
- BeanNameAware.setBeanName(String name):如果Bean实现了
BeanNameAware接口,一旦对Bean的依赖注入完成,Spring容器就会调用Bean的void setBeanName(String name)方法。传递的参数为Bean的id; - BeanClassLoaderAware.setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader):如果Bean实现了
BeanNameAware接口,会回调该方法,参数为:bean实例提供bean类装载器; - BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory):如果Bean实现了
BeanFactoryAware接口,会回调该方法,参数为:实例化该bean的BeanFactory; - ApplicationContextAware.setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext):如果Bean实现了
ApplicationContextAware接口,容器会调用该方法,将bean所在应用的上下文引用传入; - BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName):如果Bean实现了
BeanPostProcessor接口,此时会调用该接口的Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException方法; - @PostConstruct:如果Bean有该注解方法,Web容器会调用该初始化方法;参见另一篇文章:Spring Java EE @PostConstruct @PreDestroy Servlet生命周期的注解;
- InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet():如果Bean实现了
InitializingBean接口,Spring容器会调用该方法afterPropertiesSet(); - Bean的init-method方法:如果Bean在XML定义了
init-method或@Bean注解配置了initMethod的方法名称,此时会被容器进行调用; - BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName):如果Bean实现了
BeanPostProcessor接口,此时会调用该接口的Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException方法;
至此,bean已经准备就绪,可以被应用程序使用了,它将一直驻留在应用程序的上下文中,直到该应用上下文被销毁。
Bean销毁的过程
- @PreDestroy:如果Bean有该注解方法,Web容器销毁时会调用该销毁方法;参见另一篇文章:Spring Java EE @PostConstruct @PreDestroy Servlet生命周期的注解;
- DisposableBean.destroy():如果Bean实现了
DisposableBean接口,会调用该接口定义的destroy()方法; - Bean的destroy-method方法:如果Bean在XML定义了
destroy-method或@Bean注解配置了destroyMethod的方法名称,此时会被容器进行调用;
Bean装配的方式
Spring提供了3中装配Bean的方式,分别是:
- 隐式的bean发现和自动装配;
- 在Java类中进行显示配置;
- 在XML中进行显示配置。
隐式的bean发现和自动装配:自动化装配Bean
自动化装配Bean主要是2方面:
- 组件扫描:Spring会自动发现应用上下文并创建bean;
- 自动装配:Spring自动满足bean之间的依赖。
@Component注解:表明该类会作为组件类,告知Spring为该注解类创建bean,可以通过value属性设置bean的id,不设置value属性,Spring会根据类名来指定设置bean的id,即将类名首字母小写;@Configuration和@ComponentScan注解:@Configuration表明该类作为Spring配置类;@ComponentScan注解,表示启动Sprinig组件扫描,默认会扫描与配置类相同的包;@Autowired:声明进行自动装配。
扫描与AppConfig配置类相同的包:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
public class AppConfig {
}指定组件扫描的基础包,通过value属性指定扫描基础包。如果需要更清楚的表名是设置扫描的基础包,可以使用属性basePackages:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.test.app")
public class AppConfig {
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.test.app")
public class AppConfig {
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.test.app1", "com.test.app2"})
public class AppConfig {
}通过指定包含的类或接口设置扫描的基础包:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackageClasses = {Config1.class, Config2.class})
public class AppConfig {
}通过@Autowired设置自动装配bean:
@Component
public class Compoent1 {
private Component2 component2;
// 构造器自动装配
@Autowired
public Compoent1(Component2 component2) {
this.component2 = component2;
}
// 使用属性Setter方法装配
@Autowired
public void setComponent2(Component2 component2) {
this.component2 = component2;
}
// 属性自动装配
@Autowired
private Component2 component2;
}实际上@Autowired注解可以用在类的任何方法上,效果一样,不过建议从上面中的3个中选。
通过Java类装配Bean
Java Config是配置代码,不应该包含任何业务代码和侵入到业务代码中,通常会将Java Config放到单独的包中,使其与业务逻辑代码分开。
- 创建
Java Config类的关键是在类上添加@Configuration注解; - 在
Java Config中声明bean,编写一个方法,创建所需类型的实体,并给这个方法添加@Bean注解。
默认创建的bean的ID与@Bean注解的方法名一样,也可以通过name属性指定自定义的名称。
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig() {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("org.h2.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost/~/appdatabase");
ds.setUsername("sa");
ds.setPassword("");
return ds;
}
}装配Bean依赖的方法:
- 在JavaConfig中装配Bean的依赖最简单的方式是:直接引用创建bean的方法。
- 让Spring自动装配依赖的Bean到配置方法中。这种方式引用其他的bean通常是最佳选择
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig() {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("org.h2.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost/~/appdatabase");
ds.setUsername("sa");
ds.setPassword("");
return ds;
}
/**
* 直接引用创建bean的方法
*/
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate() {
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource());
}
/**
* 让Spring自动装配依赖的Bean到配置方法中
*/
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
}通过XML装配Bean
通过XML装配Bean,要创建一个以<beans>原始为根的XML文件。
最简单的Spring XML配置文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 此处配置bean -->
</beans>混合配置装配Bean
混合配置时,需要注意的是:在自动装配时,它并不在意装配的bean来自哪里。自动装配的时候,会考虑Spring容器中所有的bean,不管它是在JavaConfig或XML中声明还是通过组件扫描获取的。
在JavaConfig中引用其他JavaConfig或引用XML
@Import注解:导入其它JavaConfig:
@Configuration
@Import({DataSourceConfig.class, JmsConfig})
public class AppConfig {
}
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
}
@Configuration
public class JmsConfig {
}@ImportResource注解:导入XML配置
@Configuration
@Import(JmsConfig)
@ImportResource("classpath:applicationContext-dataSource.xml")
public class AppConfig {
}
@Configuration
public class JmsConfig {
}在XML配置中引用其他JavaConfig
XML配置方式,可以通过<import>元素引用其它拆分的XML配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<import resource="applicationContext-dataSource.xml" />
<!-- 此处配置bean -->
</beans>通过<bean>元素导入Java配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean class="com.test.app.JmsConfig" />
<!-- 此处配置bean -->
</beans>也可同时用<import>和<bean>导入引用的配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean class="com.test.app.JmsConfig" />
<import resource="applicationContext-dataSource.xml" />
<!-- 此处配置bean -->
</beans>根配置
不管使用JavaConfig、XML配置,通常会创建一个根配置,通过根配置将多个JavaConfig或XML配置组合起来;另外在根配置中启用组件扫描:JavaConfig中使用@ComponentScan直接;XML配置中使用<context:component-sacn>。
Spring profile
Spring profile是在运行时阶段确定不同环境下创建不同类型的bean。
JavaConfig中,使用@Profile注解指定bean属于哪一个profile
@Profile应用于配置类上
只有对应profile激活时,该配置类才会创建。
下面2个例子分别针对开发环境,实际部署环境创建dataSource的Bean。
开发环境:
@Configuration
@Profile("dev")
public class DevProfileConfig {
@Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown")
public DataSource dataSource() {
}
}部署环境:
@Configuration
@Profile("prod")
public class ProdProfileConfig {
@Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown")
public DataSource dataSource() {
}
}@Profile应用于方法上
方法级别上使用@Profile注解与@Bean注解一起使用,可以将多个环境的bean声明放在同一个配置类中。没有指定profile的bean始终都会创建。
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Bean(destoryMethod = "shutDown")
@Profile("dev")
public DataSource devDataSource() {
}
@Bean(destoryMethod = "shutdown")
@Profile("prod")
public DataSource prodDataSource() {
}
}XML中,配置profile
在XML中,可以通过
这里也对应有2种设置profile方式:
- 根
元素中的profile属性; - 在根
元素中嵌套使用 元素。
根
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
profile="dev">
<jdbc:embedded-database id="dataSource" type="H2">
<jdbc:script location="classpath:schema.sql" />
<jdbc:script location="classpath:test-data.sql" />
</jdbc:embedded-database>
</beans>在根
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<beans profile="dev">
<jdbc:embedded-database id="dataSource" type="H2">
<jdbc:script location="classpath:schema.sql" />
<jdbc:script location="classpath:test-data.sql" />
</jdbc:embedded-database>
</beans>
<beans profile="prod">
<jee:jndi-lookup id="dataSource"
lazy-init="true"
jndi-name="jdbc/myDatabase"
resource-ref="true"
proxy-interface="javax.sql.DataSource" />
</beans>
</beans>激活profile
Spring通过spring.profiles.active和spring.profiles.default来确定哪个profile处于激活状态。
如果设置了spring.profiles.active属性,设定的profile是激活的;如果没有设置spring.profiles.active属性,那么Spring会查找spring.profiles.default设置的值,对应设置的profile是激活的;如果2个都没有设置的话,Spring是会创建没有定义profile的bean。
设置spring.profiles.active和spring.profiles.default方式:
- 作为DispatcherServlet的初始化参数;
- 作为Web应用的上下文参数;
- 作为JNDI条目;
- 作为环境变量;
- 作为JVM的系统属性;
- 在测试类上,使用
@ActiveProfiles注解设置。
例如Web应用web.xml设置默认的profile
<context-param>
<param-name>spring.profiles.default</param-name>
<param-value>dev</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>demo</serlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispaterServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>spring.profiles.default</param-name>
<param-value>dev</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>在测试类上使用@ActiveProfiles注解:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes=DataSourceConfig.class)
@ActiveProfiles("dev")
public class DataSourceTest {
}条件化bean
@Conditional注解:如果条件结果为true,则Spring容器则会创建这个bean,否则该bean会被忽略。
@Conditional中给定一个Class的类是实现Condition接口,该接口有一个boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata)方法。
/**
* 根据条件创建bean
*/
@Bean
@Conditional(ConditionExistCondition.class)
public ConditionBean conditionBean() {
return new ConditionBean();
}
public class ConditionExistCondition implements Condition {
// 检查条件
boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
Environment env = context.getEnvironment();
return env.containsProperty("condition");
}
}matches方法会传入2个参数:ConditionContext context和AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata。
ConditionContext 接口方法参数详解:
BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry():返回BeanDefinitionRegistry检查bean定义;ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory():返回ConfigurableListableBeanFactory可以检查bean是否存在,甚至可以探测bean的属性;Environment getEnvironment():返回Environment,检查环境变量是否存在以及环境变量的内容;ResourceLoader getResourceLoader():返回ResourceLoader加载的资源;ClassLoader getClassLoader():返回的ClassLoader加载并检查类是否存在。
AnnotatedTypeMetadata 接口方法参数详解:
该接口能够让我们检查带有@Bean注解还有其它什么注解。
boolean isAnnotated(String annotationName):是否存在待检测的注解;Map<String, Object> getAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName):获取给定注解的属性映射;Map<String, Object> getAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName, boolean classValuesAsString):获取给定注解的属性映射;MultiValueMap<String, Object> getAllAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName):获取给定注解属性的MultiMap列表;MultiValueMap<String, Object> getAllAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName, boolean classValuesAsString):获取给定注解属性的MultiMap列表。
@Profile注解本身也是用了@Conditional注解。
bean的作用域
Spring定义了多种作用域。
- Singleton单例:整个应用中,只创建bean的一个实例;
- Prototype原型:每次注入或通过Spring上下文获取bean的时候,都会创建一个新的bean的实例;
- Session会话:在Web应用中,每个会话Session只创建一个bean的实例;
- Request请求:在Web应用中,每个请求Request创建一个bean的实例。
自动扫描装配设置bean的作用域:
@Component
@Scope(ConfiguableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
public class ComponentDemo1 {
}JavaConfig设置bean的作用域:
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
public ComponentDemo1 componentDemo1() {
}
}XML配置设置bean的作用域:
<bean id="componentDemo1" class="com.demo.ComponentDemo1" scope="prototype" />@Scope注解有一个proxyMode属性
JavaConfig配置方式设置proxyMode:
- ScopedProxyMode.INTERFACES:表明代理要实现模板bean的接口,并将调用委托给实现的bean;
- ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS:表明要以生成目标类扩展的方式创建代理。
XML配置方式设置proxyMode:
XML中使用Spring aop设置代理模式:<aop:scoped-proxy>对应JavaConfig中的proxyMode。默认情况下,它会使用CGLib创建模板类的代理,我们也可以通过设置属性proxy-target-class为false,更改为基于接口的代理。
<bean id="componentDemo1" class="com.demo.ComponentDemo1" scope="session">
<aop:scoped-proxy />
</bean><bean id="componentDemo1" class="com.demo.ComponentDemo1" scope="session">
<aop:scoped-proxy proxy-target-class="false" />
</bean>运行时给Bean注入值
Spring提供2种在运行时求值的方式:
- Property placeholder:属性占位符
- SpEL:Spring表达式语言
属性占位符注入外部值
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:app.properties", encoding = "UTF-8")
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Bean
private DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(env.getProperty("jdbc.driver"));
dataSource.setJdbcUrl(env.getProperty("jdbc.url");
dataSource.setUsername(env.getProperty("jdbc.username");
dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty("jdbc.password");
return dataSource;
}
}Environment详解
通过getProperty获取配置属性值的方法,如果获取配置属性值是必须要定义的,可以使用getRequiredProperty()对应的方法:
- String getProperty(String key)
- String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue)
T getProperty(String key, Class targetType) T getProperty(String key, Class targetType, T defaultValue)
除了获取属性值外,Environment还提供了检测profile处于激活状态:
- String[] getActiveProfiles():返回激活的profile名称的数组列表;
- String[] getDefaultProfiles():返回默认的profile名称的数组列表;
- boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles):如果环境支持给定的profile,返回true。
解析属性占位符
属性占位符的使用形式:${...}。
XML配置使用属性占位符:
<bean id="compoentDemo1" class="com.demo.ComponentDemo1"
c:_name="${compoentDemo1.name}"
c:_title="${compoentDemo1.title}"
/>JavaConfig配置类中使用属性占位符:
为了使用使用占位符
@Bean
public ComponentDemo1 compoentDemo1(@Value(${compoentDemo1.name}) String name, @Value(${compoentDemo1.title}) String title) {
return new ComponentDemo1(name, title);
}参考文章
《Spring实战(第4版)》
Spring Bean Life Cycle Tutorial
Spring Bean的生命周期(非常详细)